Python is a programming language that lets you work more quickly and integrate your systems more effectively. You can learn to use Python and see almost immediate gains in productivity and lower maintenance costs. We will use Python in the class for simulation and analysis. Matlab was (and still is) the dominant tool of choice for signal processing researchers. However, with the growth of open-source software and machine learning in particular, Python has begun to supplant Matlab.
The easiest way to install Python is through Anaconda: anaconda.com or Miniconda: miniconda.com. This works for Windows, Mac, and Linux, and can help you install all the required packages.
It is recommended to download and install the Python 3.7 version.
IPython is a command shell for interactive computing in multiple programming languages, especially focused on the Python programming language, that offers enhanced introspection, rich media, additional shell syntax, tab completion, and rich history.
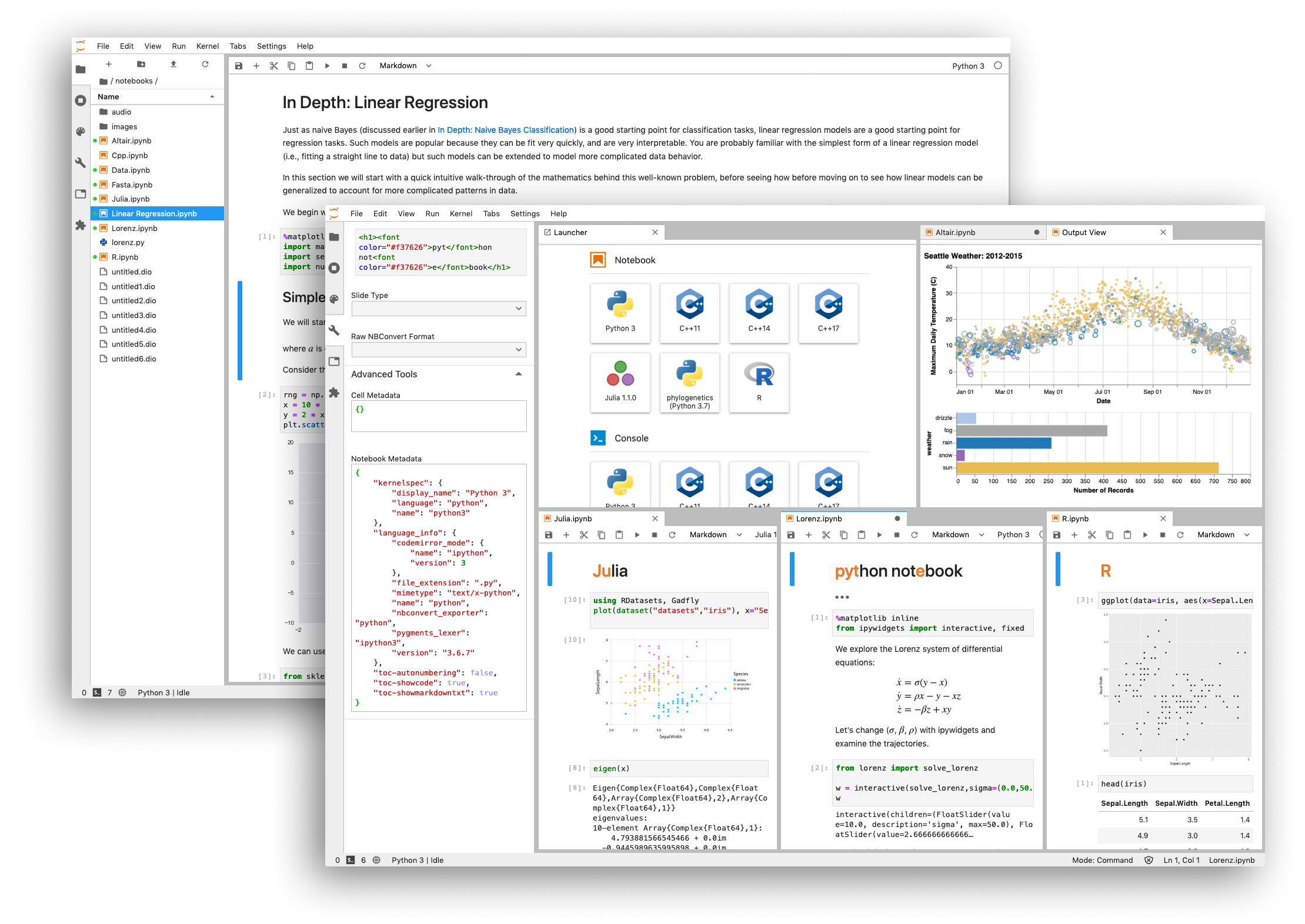
Jupyter Notebook is a web-based interactive computational environment where you can combine code execution, text, mathematics, plots and rich media into a single document:

A short, interactive introduction to Python and Jupyter Notebook is available here: [html] [Notebook file]
JupyterLab is a web-based interactive development environment for Jupyter notebooks, code, and data. JupyterLab is flexible: configure and arrange the user interface to support a wide range of workflows in data science, scientific computing, and machine learning. JupyterLab is extensible and modular: write plugins that add new components and integrate with existing ones.
NumPy is the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python. It contains among other things:
The SciPy library is a collection of numerical algorithms and domain-specific toolboxes, including signal processing, optimization, statistics and much more.
Matplotlib is a python 2D plotting library which produces publication quality figures in a variety of hardcopy formats and interactive environments across platforms.
“Python for Signal Processing” By José Unpingco. Available for students through UT Library: Link
Python Bootcamp by Josh Bloom and Fernando Perez: Link
Introduction to Python (general): Link
A Crash Course in Python for Scientists: Link
Scientific Computing with Python: Link
Numpy tutorial: Link
Signal Processing Reference Guide: Link
Numpy for Matlab users: Link
Generated by jon-doc